Plant-based sources for Iron
Iron is vital for red blood cell production, supporting energy and immunity. Iron deficiency can lead to anemia, resulting in symptoms like fatigue, weakness, and decreased immune function due to a lack of red blood cell production. Consuming vitamin C-rich foods alongside these sources enhances iron absorption. Additionally, using cast-iron cookware and focusing on diverse, iron-rich foods helps maintain adequate iron levels in a vegan diet.
Plant-based sources for Calcium
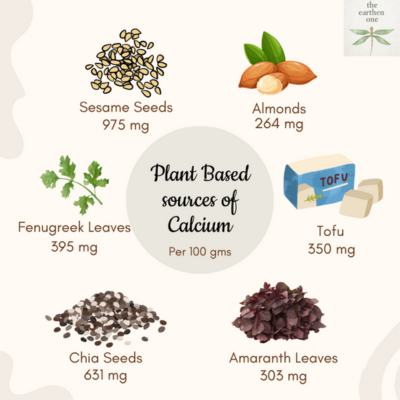
Calcium is important because lack of it might lead to a calcium deficiency can lead to osteoporosis, weakened bones, and an increased risk of fractures due to insufficient mineralization and bone density. Incorporating calcium rich foods into a balanced diet helps vegans meet their calcium needs.
Protein
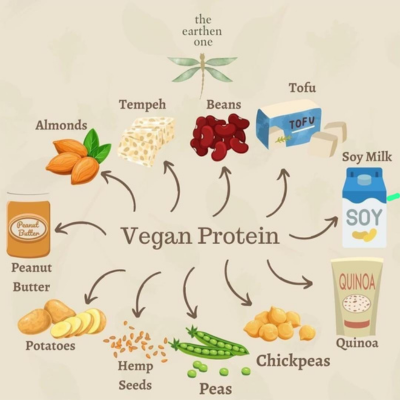
Vegans can meet their protein needs through various plant-based sources. Combining different protein sources throughout the day ensures a complete amino acid profile. Additionally, fortified foods and plant-based protein powders offer convenient options.
Magnesium
Magnesium can be acquired from various plant-based foods. A deficiency in magnesium can lead to muscle cramps, weakness, and irregular heartbeat due to its role in muscle and nerve function. Incorporating proper proportions of magnesium helps to fulfill magnesium requirements for vegans.
Phosphorus
A deficiency in phosphorus can lead to weakened bone density and strength, as phosphorus is essential for bone mineralization and structure. Phosphorus can also be provided from bread, brown rice, and oats
Vitamin A
A deficiency in vitamin A can lead to vision problems, including night blindness, and compromise the immune system’s function such as increased susceptibility to infections, complications in pregnancy and altered mucosal immunity. Vitamin A can be acquired through beta-carotene-rich foods. Incorporating these foods into daily meals ensures a sufficient intake of Vitamin A for vegans.
Omega 3
A deficiency in omega-3 fatty acids can lead to impaired brain function and cardiovascular issues due to their crucial role in neurological health and heart function.Plant based Omega-3 can be obtained from fatty acids, specifically ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). Food that provides a plant-based form of omega-3, which the body can convert into EPA and DHA. Consider algae-based supplements for direct EPA and DHA intake in a vegan diet.
Vitamin E

A deficiency in vitamin E can lead to neurological issues, muscle weakness, impaired vision, and a weakened immune system. Insufficient vitamin E intake may also result in nerve damage and an increased risk of heart disease due to its role in protecting cells from oxidative damage.
Vitamin B12

Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to anemia, fatigue, weakness, neurological issues like tingling or numbness in extremities, difficulty walking, memory problems, and mood disturbances. If left untreated, severe deficiency can result in irreversible nerve damage and complications affecting the nervous system.
Nutrition
Plant-based sources for Iron

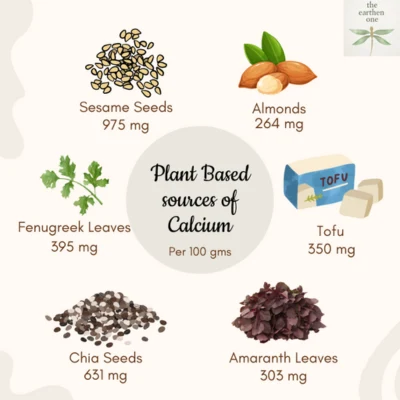
Plant-based sources for Calcium
Protein
Vegans can meet their protein needs through various plant-based sources. Combining different protein sources throughout the day ensures a complete amino acid profile. Additionally, fortified foods and plant-based protein powders offer convenient options.


Magnesium
Magnesium can be acquired from various plant-based foods. A deficiency in magnesium can lead to muscle cramps, weakness, and irregular heartbeat due to its role in muscle and nerve function. Incorporating proper proportions of magnesium helps to fulfill magnesium requirements for vegans.
Phosphorus


Vitamin A
Omega 3


Vitamin E
Vitamin B12


